|^·<×>·v| |
A.1 |
|
What are DRGs?
|
1 |
1
Cf.
Fetter et al. [DRGs, 1980];
Fetter et al. [DRGs, 1991];
Iezzoni [Risk Adjustment, 1994];
Fischer [PCS, 1997];
Fischer [DRG+Pflege, 2002].
|
|
DRG systems |
The abbreviation DRG signifies «Diagnosis Related Groups».1
DRG systems
are medico-economical
patient classification systems.
In acute hospitals, they allow for classification of
hospital stays into a limited number of clinically defined groups
with costs of treatment as similar as possible. |
2 |
|
|
Case groups
and grouping criteria |
A DRG system consists of a list of individual DRGs
which are labelled and codeable case groups.
DRGs are defined by grouping criteria
in a comprehensive framework of rules.
Specific figures and prices
can be attributed to each DRG. |
3 |
|
|
Construction |
To create DRG lists, list of diagnoses have been usually
roughly structured and aggregated by groups of physicians.
The fine-tuning was then elaborated
often based on statistical analyses of cost data.
(Because in the early days of the development of DRGs
almost no cost data was available,
length of stay was used as a proxy for cost.) |
4 |
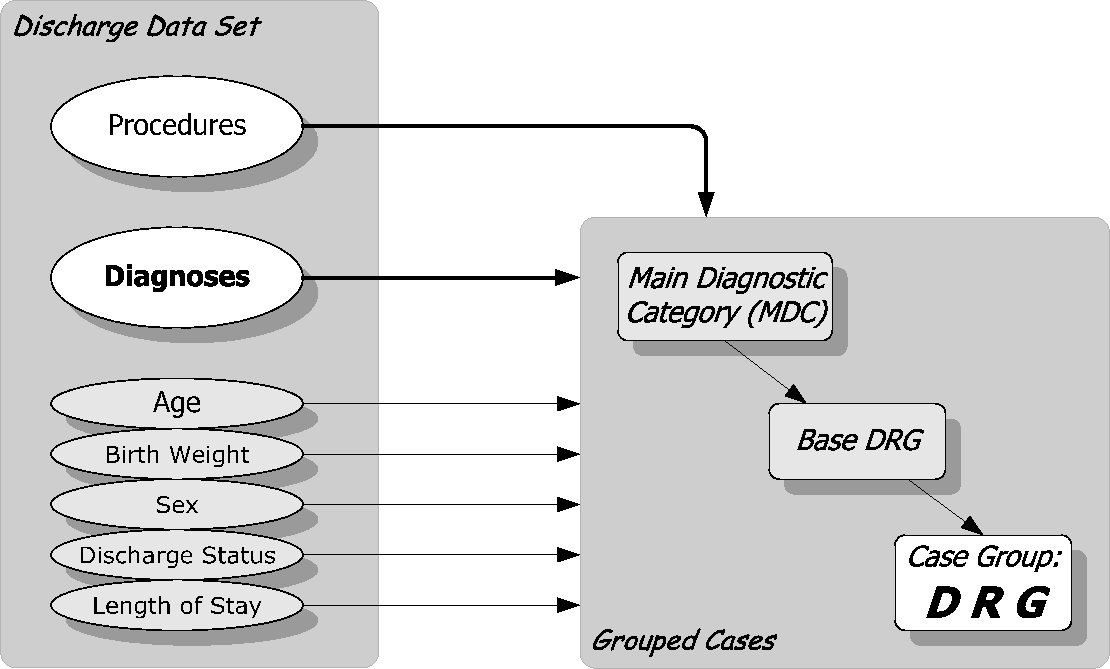
Table 1:
Assignment of DRGs based on data from the discharge data set
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
Source: Fischer [DRG-CH, 2004]. |
|
|
|
Use of routine data |
The development of DRG systems started in the late 70s in the
United States.
One of the framework conditions was that only data routinely
collected was admissible.
At that time, the discharge data set in US hospitals contained
the following clinical data:
[Table 1]
-
principal and secondary medical diagnoses
-
surgical and diagnostic procedures
-
age and sex of patients
|
6 |
|
|
|
This data
– together with the birth weight of newborns,
which was later added –
has ever since been the backbone of
grouping criteria
in DRG systems worldwide.
|
7 |
|
|
Hospital products |
Such information made it possible to define a part of the products
rendered by hospitals.
While the first DRGs had been originally defined as part of a
quality control project, they soon came to reflect the money
value of treatments, and were used in price lists.
1983, "Medicare" of United States
was the first insurance provider to use
DRGs as a basis for reimbursement of hospital stays.
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
References |
|
|
| -
Fetter et al.
- DRGs
1980
| Fetter RB, Shin Y, Freeman JL, Averill RF, Thompson JD. Casemix definition by Diagnosis Related Groups. In: Medical Care 1980(18): S1–S53. | 9 |
|
| -
Fetter et al.
- DRGs
1991
| Fetter RB, Brand A, Dianne G [Hrsg.]. DRGs, Their Design and Development. Ann Arbor (Health Administration Press) 1991: 341 pp. | 10 |
|
| -
Fischer
- PCS
1997
| Fischer W. Patientenklassifikationssysteme zur Bildung von Behandlungsfallgruppen im stationären Bereich. Prinzipien und Beispiele. Bern und Wolfertswil (ZIM) 1997: 514 pp. Auszüge:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / PCS-Buch-9701-Info.htm. | 11 |
|
| -
Fischer
- DRG+Pflege
2002
| Fischer W. Diagnosis Related Groups (DRGs) und Pflege. Grundlagen, Codierungssysteme, Integrationsmöglichkeiten. Bern (Huber) 2002: 472 pp. Auszüge:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / DRG-Pflege-0112-Info.htm. | 12 |
|
| -
Fischer
- DRG-CH
2004
| Fischer W. Gesucht: Ein DRG-System für die Schweiz. Kurzer Überblick zum Beginn der Arbeiten am SwissDRG-Projekt. In: Competence 2004/5: 4–8. Internet:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / artikel / DRG-CH-Modellwahl-0404.htm. | 13 |
|
| -
Iezzoni
- Risk Adjustment
1994
| Iezzoni LI [Hrsg.]. Risk Adjustment for Measuring Health Care Outcomes. Ann Arbor (Health Administration Press) 1994: 423 pp. | 14 |
![[print]](../PIC/e-div/print.gif)
![[pdf icon]](../PIC/e-div/pdf.gif) Whole Text as pdf file
(1020 KB)
Whole Text as pdf file
(1020 KB) Kurz-Info: Was sind DRGs?
Kurz-Info: Was sind DRGs? DRG-Prinzipien
DRG-Prinzipien DRG-Verwandtschaftsprobleme
DRG-Verwandtschaftsprobleme